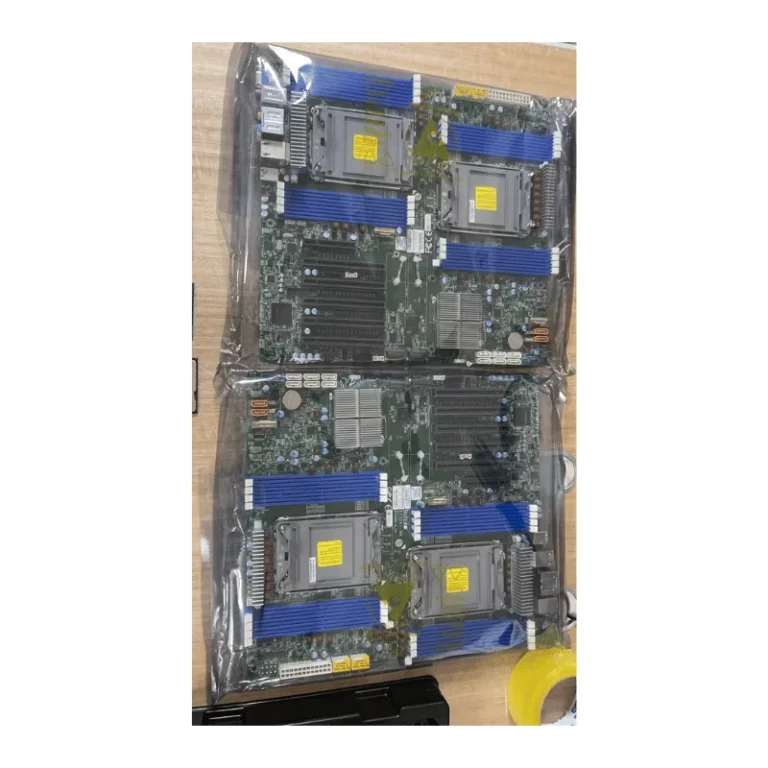
People often want to know the big differences between a motherboard for server computer and a desktop motherboard. The type you pick changes how well your computer works and how long it lasts.
Desktop motherboards make up 71.3% of the market, which is worth USD 37,191.33 million.
Server motherboards are selling more each year, and by 2026, over 16 million will be shipped worldwide.
Motherboards link all the parts in a computer. New features like PCIe 5.0 and DDR5 memory make fast computers even quicker. Strong builds and IoT support help servers work in hard places. This article will compare them so readers can make a smart choice.
Key Takeaways
Pick a motherboard that fits what you need. Server motherboards work best for big jobs. Desktop motherboards are good for daily use. Server motherboards can use more than one CPU and ECC memory. This makes them more reliable and faster for important jobs. Desktop motherboards are easy to use. They are made for gaming and normal tasks. This makes them great for home or office. Think about how much you want to upgrade later. Server motherboards have more slots for upgrades. Desktop motherboards cover simple needs. Server motherboards cost more at first. But they last longer and can grow with your needs.
Key Differences Between Server and Desktop Motherboards

Comparison Overview
You should pick a server motherboard or a desktop motherboard based on what you need. Server motherboards have features for tough jobs. Desktop motherboards are made for daily use and fun. The table below shows the biggest hardware differences.
Feature | Server Motherboard | Desktop Motherboard |
|---|---|---|
CPU Support | Supports multiple CPUs for parallel processing | Supports a single CPU |
Memory Type | ECC Registered DIMMs with higher capacities | Non-ECC DIMMs, lower max RAM capacity |
Expansion Slots | More PCIe slots for networking, storage controllers | Fewer, focused mostly on graphics and peripherals |
Build Focus | Stability, uptime, manageability | Gaming, multimedia, general-purpose use |
Network Connectivity | Multiple high-speed LAN ports (10GbE or more) | Usually 1-2 standard Ethernet ports |
Form Factor | Larger sizes (E-ATX, SSI-EEB) for expandability | Standard sizes (ATX, Micro-ATX, Mini-ITX) |
Power Delivery | Robust power phases with server-grade VRMs | Less robust, consumer-grade power phases |
BIOS/UEFI Features | Remote management, server-specific firmware features | User-friendly BIOS with overclock and gaming settings |
This table shows that server motherboards are made for being reliable, growing bigger, and working fast. Desktop motherboards are easier to use and good for normal computer work.
Main Distinctions
Server motherboards are special because they use ECC memory. ECC memory finds and fixes mistakes in data. This makes the server more reliable and helps stop data loss. Most desktop motherboards do not use ECC memory. This means they are not as good for important jobs.
Server motherboards can use more than one CPU at the same time. This helps servers do more work and get bigger for things like virtualization and database jobs. Desktop motherboards usually only use one CPU. This means they cannot grow as much.
Note: Server motherboards often have extra power supplies and RAID. These features help protect the server if something breaks. They keep the server working without stopping.
Server motherboards have more slots for extra network cards and storage. This helps big companies add more parts later. Desktop motherboards have fewer slots. They are mostly for graphics and simple add-ons.
Server motherboards are built to stay on and work well for a long time. They use strong parts and have special tools like IPMI. IPMI lets people check and control the server from far away. These things help servers keep running and make them easy to manage.
Desktop motherboards are made for people who play games, watch videos, or do office work. They have easy BIOS settings and work with lots of popular parts. But they are not as strong or able to grow as server motherboards.
What Is a Motherboard for Server Computer?

Definition and Role
A motherboard for server computer is the main board inside a server. It connects all the server parts together in one system. This motherboard is made to be reliable and cool. It has strong input and output connections. It is different from motherboards for regular computers. It can handle heavy work and helps servers run well.
The motherboard for server computer links the CPU, memory, storage, and network ports. These parts talk to each other through the motherboard. It helps with important jobs like data processing and memory management. The design of the motherboard changes how well the server works and grows. Picking the right motherboard helps build servers for simple or hard jobs.
Core Features of Server Motherboards
A motherboard for server computer has special features for tough jobs. Most server motherboards use ECC memory. ECC memory checks and fixes errors to keep data safe. Some models, like the 11DPI-N and 11DPL-I, let you use more than one CPU. This makes the server faster and able to grow. These motherboards have extra PCIe slots for network cards and storage.
Server motherboards have advanced tools for remote monitoring and control. IT teams can manage servers from far away without being there.
A motherboard for server computer also supports RAID setups. RAID protects data if a drive stops working. Strong power and cooling systems keep the server running for a long time. The 12DAI-N6 and 2SEEP models work for different jobs. The 3DE and 3DGQ motherboards have special features for unique needs.
Typical Use Cases
Companies use a motherboard for server computer in many places. Data centers use these motherboards for cloud services and storing lots of data. Businesses pick server motherboards for jobs like virtualization, real-time analytics, and database management. These motherboards are good for places that need to work all the time.
A motherboard for server computer is also used for web hosting, science research, and business planning. It supports more than one CPU and lots of ECC memory. This makes it great for hard jobs. Server motherboards help keep important systems working and ready for big tasks.
Understanding Desktop Motherboards
Definition and Role
Desktop motherboards are the main boards inside desktop computers. They connect the processor, memory, storage, and other parts together. These motherboards help computers run games, programs, and use the internet. Desktop motherboards are made to be easy for people to use and upgrade. Most only support one processor and regular memory. People use them at home, in schools, and in small offices.
Desktop motherboards are not the same as server motherboards. They are made for personal use and fun activities. They do not have special error correction or support for more than one processor. The layout makes it simple to add things like graphics cards and storage drives.
Key Features of Desktop Motherboards
Desktop motherboards have many features for daily computer use. Most have slots for graphics cards and extra memory. You can find USB ports, audio jacks, and network ports on them. The BIOS lets users change settings easily. Some desktop motherboards let you overclock for better speed.
Tip: Desktop motherboards come in sizes like ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. These sizes fit different computer cases and needs.
Here is a table that shows common features of desktop motherboards:
Feature | Description |
|---|---|
CPU Socket | Works with popular desktop processors |
Memory Slots | Holds regular desktop RAM |
Expansion Slots | For graphics, sound, and network cards |
Storage Connectors | SATA and M.2 for hard drives and SSDs |
USB Ports | Connects things like keyboards and mice |
Audio Jacks | For speakers and microphones |
Desktop motherboards make building or upgrading a computer simple. Most work with many brands of computer parts.
Common Applications
People use desktop motherboards in many ways. Home users build gaming computers with them. Students use them for homework and online classes. Offices use desktop motherboards for typing and making spreadsheets. Artists and designers use them for editing photos and videos.
Desktop motherboards also run computers for small businesses. Many are used in point-of-sale systems and office networks. Unlike server motherboards, desktop motherboards are for personal and small group jobs. They give users good value and flexibility for everyday tasks.
Server Motherboards vs Desktop Motherboards: Feature Comparison
Performance and Processors
Server motherboards are made for tough jobs. They can use more than one CPU. This helps servers run many virtual machines at once. They also handle big jobs like company databases. Desktop motherboards usually use just one processor. This is fine for home or office work. The table below shows how they are different:
Feature | Server Motherboards | Desktop Motherboards |
|---|---|---|
Core Count | Higher core counts | Lower core counts |
ECC Memory | Supported | Not supported |
PCIe Lanes | More PCIe lanes | Fewer PCIe lanes |
Workload Handling | Designed for heavy workloads | Designed for consumer-level applications |
Reliability | Built for reliability in critical tasks | Standard reliability |
Server motherboards are made to not make mistakes. They are used in data centers and places that need strong computers. Desktop motherboards are built for speed in games and daily use.
Memory and Expansion
Server motherboards can use more memory than desktop ones. They use ECC memory, which finds and fixes errors. This is important for running virtual machines. Desktop motherboards use normal memory and have fewer slots.
Server motherboards can hold more memory.
ECC memory helps find and fix mistakes.
Server motherboards have lots of ways to connect to networks and storage.
Desktop motherboards have slots for graphics cards and other things people use.
Server motherboards let you add more network cards and storage. This helps servers grow if a business gets bigger.
Storage and RAID
Server and desktop motherboards have different storage options. Server motherboards can use many drives and RAID. RAID keeps data safe and makes things faster. Desktop motherboards usually use one or two drives. They do not have as many RAID features.
Feature | Server Motherboards | Desktop Motherboards |
|---|---|---|
Number of Drives | Multiple drives configured in RAID setups | Typically one or two drives |
RAID Support | Onboard RAID hardware or add-on cards | Limited or no RAID support |
Data Redundancy | High redundancy to prevent data loss | Minimal redundancy |
Performance Optimization | Enhanced read/write performance through RAID | Standard performance |
Intended Use | Designed for 24/7 operation in data-intensive environments | General use, not optimized for constant load |
Server motherboards have many SATA III ports for fast data. These features are good for servers that move lots of data.
Connectivity and Slots
How a motherboard connects to other parts is important. Server motherboards have many PCIe slots. These are for network cards, RAID controllers, and other add-ons. This helps servers talk to many devices.
Expansion slots are needed for adding network cards and RAID controllers.
Servers need enough slots for all the cards they will use.
Server motherboards focus on connecting to networks and storage.
They have many PCIe slots for special server cards.
Desktop motherboards have fewer slots, mostly for graphics and simple add-ons.
Modern motherboards use PCI, PCI-X, and PCI Express slots. PCI Express x16 slots are used for graphics cards and are very fast. Server motherboards often have many fast network ports. This helps with lots of network traffic.
Feature | Server Motherboards | Desktop Motherboards |
|---|---|---|
PCIe Slots | Multiple for high-speed network and RAID | Fewer, typically for graphics and basic expansion |
Networking Connectivity | Enhanced options for networking capabilities | Standard options for home use |
Expandability | Designed for extensive expansion with add-in cards | Limited expansion capabilities |
Reliability and Uptime
Reliability is a big difference between server and desktop motherboards. Server motherboards are made to be stable and run all the time. They use strong parts and good cooling. This helps them last longer and work in important places.
Server motherboards have features to help them stay on, like remote checks and error fixing. Desktop motherboards are made for many uses and good speed. They are not as reliable as server motherboards.
Tip: Server motherboards are best for businesses that need computers to run all day.
Security and Management
Server motherboards have special security and management tools. They let IT teams control servers from far away. They also have special firmware for more settings.
Feature Type | Server Motherboards | Desktop Motherboards |
|---|---|---|
Remote Management | Yes, includes remote management features | No, focuses on user-friendly settings |
BIOS/UEFI Features | Server-specific firmware features | User-friendly BIOS with overclock and gaming settings |
Server motherboards keep data safe and protect systems during important jobs. Desktop motherboards have easy settings for home users but do not have as many security features.
Compatibility and Form Factors
How a motherboard fits in a computer is important. Server motherboards often have two CPU sockets. This gives them more power for hard jobs. They use ECC memory and have strong network features. This makes them good for data centers and web hosting.
Server motherboards can use two CPUs for big jobs.
ECC memory keeps data safe in servers.
Strong network features are good for hard jobs.
Desktop motherboards use one CPU.
Desktop motherboards do not focus on ECC memory or strong networks.
Server motherboards are bigger so you can add more parts and cooling. Desktop motherboards use sizes like ATX, Micro-ATX, and Mini-ITX. These fit in most home and office computers.
Note: Pick the right motherboard for what you need. Servers need more power, to be reliable, and to grow. Desktops need to be easy to use and flexible.
Cost and Value of Motherboards
Price Differences
How much a motherboard costs depends on what it can do and what it is for. Server motherboards are usually more expensive than desktop ones. They cost more because they have special parts and extra features. A server motherboard can use more than one processor, ECC memory, and has more slots for adding things. These features help servers do hard jobs and keep data safe.
The table below shows how much each type usually costs:
Type | Typical Price Range | Key Features Included |
|---|---|---|
Server Motherboard | $300 – $900+ | ECC memory, multi-CPU, RAID, remote management |
Desktop Motherboard | $80 – $350 | Single CPU, non-ECC memory, basic expansion |
A server motherboard costs more at first, but it is stronger and has more options. Desktop motherboards are cheaper and good for home or office computers.
Note: Companies pick server motherboards for important jobs. Spending more money helps keep computers working well for a long time.
Long-Term Value
A server gives good value over time because it is strong and can grow. Companies need servers to run important programs and save data. The server motherboard helps the server stay on and not break down. This means there are fewer problems and less money spent fixing things.
A server also works better for big jobs. Good server motherboards let you add more memory or processors later. This means you do not have to buy a new server if you need more power.
Desktop motherboards are great for home computers and small offices. They work well for normal jobs. But they might not let you add more parts or do really hard jobs like a server.
A server helps companies save money in the long run. Strong parts mean less chance of losing data and fewer repairs. The server motherboard has features that help computers keep working.
Tip: Think about how much you will spend over many years when picking a desktop or server. A server might cost more at first, but it can be a better deal because it works better and lasts longer.
Choosing the Right Motherboard
For Home and Office Users
Home and office users need to pick the right motherboard for their needs. Desktop motherboards are good for things like browsing, playing games, and office work. They are easy to upgrade and fit in most computer cases. Before buying, users should check the size, socket type, and how much memory it can hold. The table below shows how server and desktop motherboards are different for home and office use:
Feature | Server Motherboards | Desktop Motherboards |
|---|---|---|
Purpose | Stability, heavy workloads | General-purpose, individual users |
Form Factor | Larger, more components | Standard sizes, easy fit |
Processor Support | Multiple CPUs, server-grade | Consumer-grade, single CPU |
Memory Configuration | High capacity, ECC memory | Standard RAM, no ECC |
Expansion Slots | Many for networking and storage | Mix for graphics and peripherals |
Reliability Features | Redundant components | Standard reliability |
Intended Use | Enterprise applications | Gaming, content creation, daily tasks |
Some people make mistakes by picking a motherboard that does not fit what they need. Desktop motherboards are best for most homes and offices.
For Business and Server Needs
Businesses need servers that can do hard jobs and stay on all the time. A good server motherboard uses ECC memory, more than one processor, and has lots of slots for extra cards. Companies want motherboards that are strong, can grow, and have fast network ports. Here are important things for business users to think about:
Memory support, like ECC and registered memory.
Enough slots for lots of memory.
Extra slots for fast cards.
Works with many kinds of processors.
Strong parts for better reliability.
Can add more parts later.
ECC memory keeps data safe.
Fast network ports for quick connections.
A server motherboard helps the computer work better and keeps data safe. Experts can help companies pick the best motherboard for their needs.
Practical Scenarios
Server motherboards are made to run all the time. ECC memory and RAID help protect data and keep computers working in big companies.
A server is best for data centers, web hosting, and science jobs. Desktop motherboards are good for games, office work, and creative projects. People should check the chipset, size, socket, memory, slots, and network features before buying. Getting advice from experts helps people pick the right motherboard for their computer.
The table below shows the biggest differences between server and desktop motherboards. Server motherboards can use more RAM, ECC memory, and have extra slots for adding cards. Desktop motherboards are made for simple jobs and use less power.
Feature | Server Motherboards | Desktop Motherboards |
|---|---|---|
RAM Capacity | Over 1 TB | Up to 256GB |
Reliability | 24/7 uptime, redundancy | Basic reliability |
Expansion Slots | Many for peripherals | Limited for basic needs |
Experts say people should think about what they need the computer for. They should also check if the CPU fits, the size, the chipset, and how many slots there are. Picking the right motherboard helps the computer work better and last longer.
FAQ
What is ECC memory, and why do server motherboards use it?
ECC memory means Error-Correcting Code memory. Server motherboards use ECC memory because it can find mistakes in data and fix them. This helps servers keep working well and keeps important data safe.
Can a desktop motherboard be used in a server?
A desktop motherboard can do simple server jobs. It does not have things like ECC memory or more than one processor. Companies pick server motherboards for hard work and to make sure things run well.
Why do server motherboards have more PCIe slots?
Server motherboards have extra PCIe slots for network cards and storage controllers. These slots let servers connect to more things and grow when a business gets bigger.
What is remote management on server motherboards?
Remote management lets IT teams check and control servers from far away. Server motherboards have tools like IPMI. These tools help manage servers without being in the same place.
How does RAID improve server reliability?
RAID means Redundant Array of Independent Disks. Server motherboards use RAID to put many drives together. This keeps data safe if one drive breaks and makes things faster for big jobs.