16-12-2024
1. What Are the Features to Look for in a Server with 20TB of Storage?
When selecting a server with 20TB of storage, businesses must consider several features to ensure it meets their requirements. A server’s performance, storage capacity, and scalability are critical factors that can directly affect your operations.


Key Features to Consider:
- Storage Type:
- HDD vs. SSD: HDDs are cost-effective and ideal for bulk storage, while SSDs offer faster read/write speeds but are more expensive. Many businesses opt for hybrid setups (HDD + SSD) to balance cost and performance.
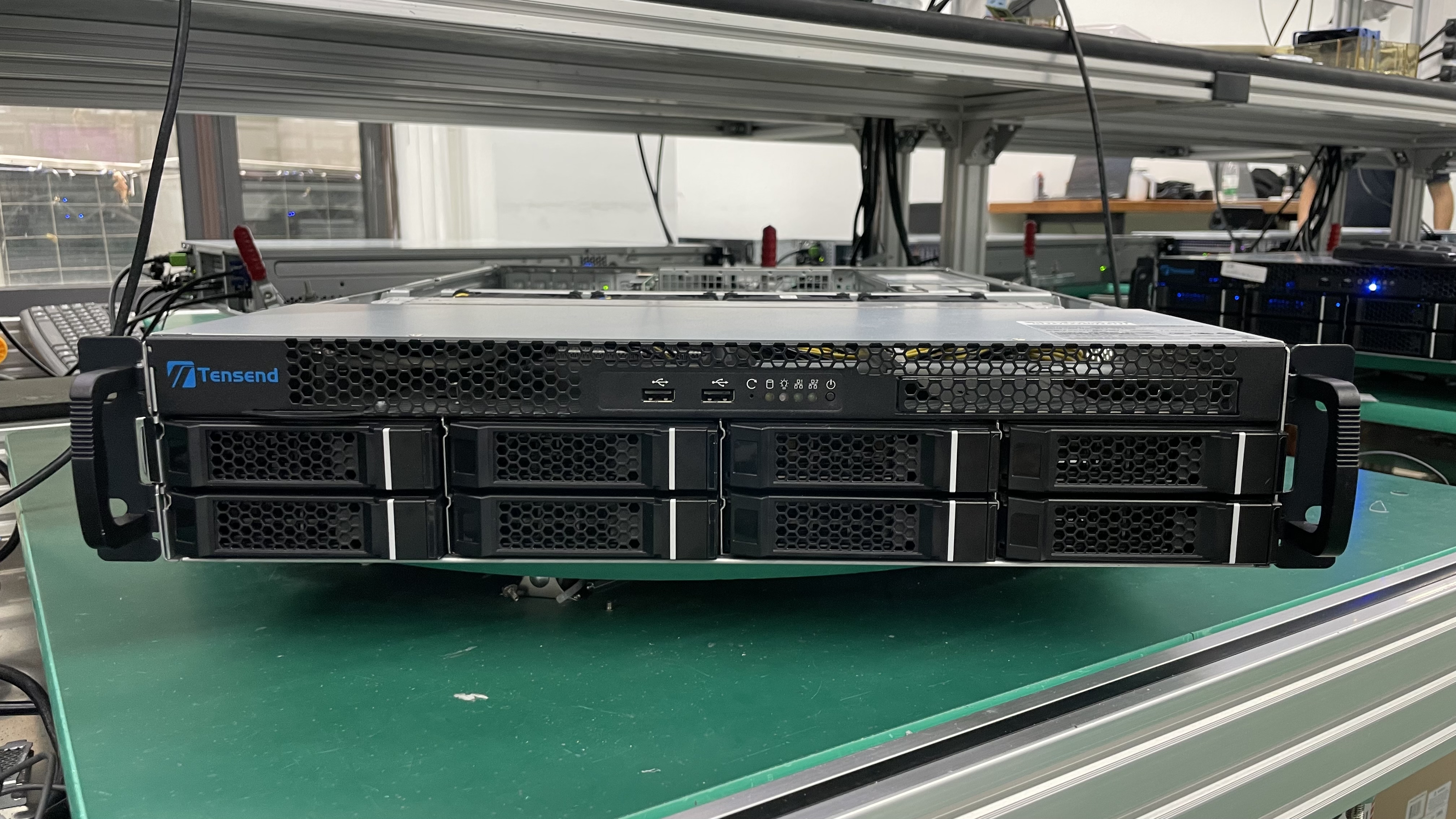
- Form Factor:
- For businesses with limited space, a rackmount storage server is an excellent choice. These compact, mountable servers maximize storage without taking up too much room.
- Redundancy and Reliability:
- RAID configurations (such as RAID 5 or RAID 6) ensure data redundancy and prevent data loss in case of hardware failure.
- ECC (Error-Correcting Code) memory enhances reliability by detecting and correcting memory errors.
- Scalability:
- A server with 20TB of storage should support expansion. For instance, if your storage needs grow, you might consider upgrading to a 100 TB storage server or even a 200 TB storage server.
- Connectivity:
- Ensure the server has sufficient I/O ports, such as USB, Ethernet, and PCIe slots, to accommodate your business needs.
- Power Efficiency:
- Modern servers are designed to be energy-efficient, reducing operational costs over time. Look for servers with ENERGY STAR certifications.
Conclusion:
A 4U storage server is often a top choice for businesses that prioritize storage capacity, reliability, and scalability. For smaller enterprises, a cheap storage server with 20TB of capacity could suffice, but ensure it meets your long-term data requirements.
2. How Does a 20TB Storage Server Compare to Larger Options Like 100TB or 200TB?
When deciding between a 20TB storage server and larger options like 100TB storage server or 200TB storage server, it’s essential to evaluate your current and future data storage needs. Let’s examine the differences.
Storage Capacity Comparison:
| Server Size | Best Use Cases | Cost Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 20TB | Small to medium-sized businesses, file sharing, website hosting, backups | Affordable; entry-level option |
| 100TB | Data-intensive applications, video editing, and large database management | Moderate; suitable for growing needs |
| 200TB or more | Enterprise-level storage, AI/ML workloads, and archival storage for large datasets | High initial cost but future-proofing |
Key Factors to Consider:
- Scalability: If your data grows consistently, starting with a 20TB storage server that supports expansion might be a better option than investing in a larger server upfront.
- Performance: Larger servers often come with advanced features like NVMe SSDs, high-speed processors, and more RAM, which can improve overall performance.
- Cost Efficiency: While high storage dedicated servers like 100TB or 200TB options have higher upfront costs, they often offer better cost-per-terabyte ratios.
Conclusion:
A server with 20TB of storage is an excellent starting point for businesses with moderate data requirements. However, for industries like media production or research, upgrading to a larger storage capacity may be inevitable as data demands increase.
3. How Can You Optimize the Performance of a Server with 20TB of Storage?
Owning a server with 20TB of storage is only the beginning. To maximize its performance, you need to optimize its configuration and manage resources effectively.
Key Optimization Strategies:
- Use RAID Configurations:
- RAID 5 or RAID 10 is ideal for balancing performance and redundancy. RAID setups distribute data across multiple drives, preventing downtime in case of a disk failure.
- Upgrade Network Infrastructure:
- A high storage dedicated server requires a strong network backbone. Invest in gigabit or 10GbE connections to ensure fast data transfer rates.
- Enable Caching:
- Utilize SSD caching to improve read/write speeds for frequently accessed data. Many servers allow SSDs to serve as cache layers for HDD storage.
- Monitor and Maintain:
- Regularly monitor server performance through tools like Windows Server Manager or Linux monitoring utilities.
- Proactively replace aging hard drives to prevent downtime.
- Leverage Virtualization:
- By virtualizing your server with 20TB of storage, you can run multiple environments on the same hardware, improving resource utilization.
Real-World Example:
A media production company using a storage dedicated server for video editing achieved a 30% improvement in workflow efficiency by upgrading to 10GbE networking and enabling SSD caching for frequently accessed files.
4. What Are the Best Use Cases for a Server with 20TB of Storage?
A 20TB storage server is versatile and can support a wide range of applications. Here are some common use cases:
Use Case 1: File Sharing and Collaboration
A server with 20TB of storage is perfect for small to medium-sized businesses that need a centralized platform for file sharing. Employees can access, modify, and share files in real-time, boosting productivity.
Use Case 2: Backup and Disaster Recovery
With 20TB of storage, businesses can maintain regular backups of critical data. Using RAID or cloud integration, these servers ensure data is protected against hardware failures or cyberattacks.
Use Case 3: Media Production
Media professionals often deal with high-resolution files that require significant storage. A rackmount storage server with 20TB can store raw footage, edited files, and final exports efficiently.
Use Case 4: Hosting Websites or Applications
20TB of storage is ample for hosting websites, applications, or databases. This storage capacity ensures fast loading times and room for growth.
Use Case 5: Research and Analytics
Organizations conducting research or data analytics can use a cheap storage server to store large datasets and run analysis without exceeding their budget.
5. How Does a Rackmount Server Compare to a Tower Server for 20TB Storage?
When choosing a server form factor, you’ll often decide between a rackmount storage server or a tower server. Here’s how they compare:
| Aspect | Rackmount Storage Server | Tower Server |
|---|---|---|
| Space Efficiency | Compact; fits into server racks | Bulky; takes up more physical space |
| Scalability | Easy to expand with multiple units | Limited scalability |
| Cooling | Better airflow in rack-mounted setups | May require additional cooling solutions |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | More affordable for small businesses |
Conclusion:
For businesses prioritizing scalability and space efficiency, a rackmount storage server is the best option. However, for startups or small businesses, a tower server might be more cost-effective.
6. How Much Should You Budget for a Server with 20TB of Storage?
The cost of a server with 20TB of storage depends on several factors, such as hardware specifications, brand, and additional features.
Estimated Cost Breakdown:
- Entry-Level Servers:
- Price Range: $1,500–$3,000
- Example: Cheap storage server with basic HDD configurations and RAID support.
- Mid-Range Servers:
- Price Range: $3,000–$6,000
- Example: Hybrid setups using SSDs for caching and HDDs for bulk storage.
- High-End Servers:
- Price Range: $6,000–$10,000+
- Example: High storage dedicated serverswith enterprise-grade components, NVMe drives, and advanced RAID configurations.
Additional Costs:
- Maintenance: Annual costs can range from $500–$2,000 depending on warranties and IT support.
- Power: Energy-efficient servers can save up to 40% on electricity bills annually.
Conclusion:
While a server with 20TB of storage is an investment, choosing the right configuration can maximize value and minimize long-term operating costs.