Please Do Not Judge the Functionality of a CPU Cooler by Its Shape
Please Do Not Judge the Functionality of a CPU Cooler by Its Shape
A CPU cooler dissipates heat by increasing the heat dissipation area and utilizing good thermal conductivity. It quickly transfers heat generated by electronic devices, mechanical equipment, or automobile engines into the air to achieve cooling.
A CPU cooler typically has the following characteristics:
1. Material Properties
Lightweight and excellent thermal conductivity allow the cooler to efficiently dissipate heat without adding excessive weight to the device.
Structural Design: CPU coolers usually feature multiple heat dissipation fins, which increase the surface area and improve cooling efficiency.
2. Manufacturing Process
CPU coolers can be manufactured into various shapes and sizes through extrusion, casting, cutting, and other processing techniques to meet different application needs.
3. Wide Applications
CPU coolers are widely used in computer CPUs, graphics cards, power modules, LED lighting, automotive engines, motorcycle engines, and other applications requiring heat dissipation.
CPU Cooler Performance Analysis
To ensure that critical server components (such as CPU, DIMM, VRM) operate within the appropriate temperature range, maintaining optimal performance and longevity, it is essential to monitor and collect temperature data and analyze the impact of temperature reduction.
1. CPU Cooler Design
The 1U Enhanced Volume Air-Cooled (EVAC) CPU Cooler has been optimized to achieve maximum cooling performance while maintaining the same Keep-Out Zone (KOZ) as traditional air-cooled CPU coolers.
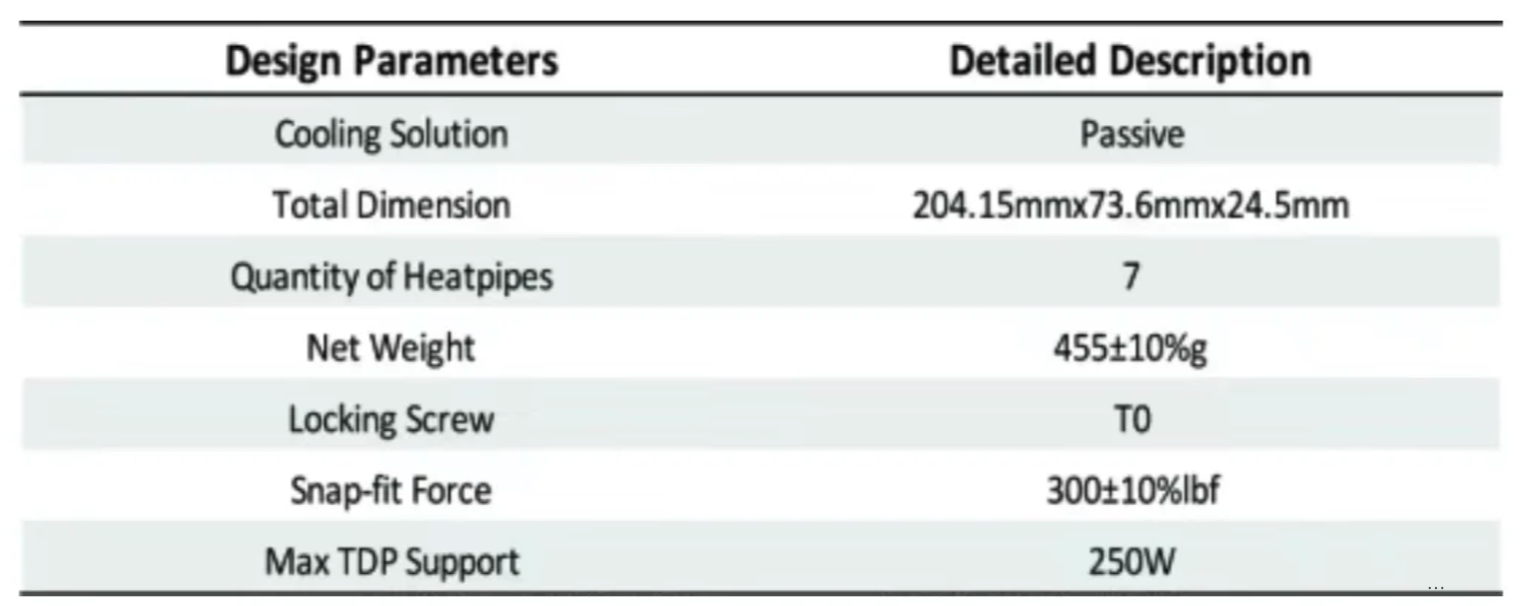
2. Selection and adoption of TIM:
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) are used to improve heat transfer efficiency between components and hot solutions. Incompatibility can cause CPU overheating. Adopting DowSIL ™ TC-5888, as a TIM, has a thermal conductivity of 5.2w/mK and dimensions of 70mm x 50mm x 0.2mm, similar to PoC [20], enhancing CPU cooling and long-term operational reliability.
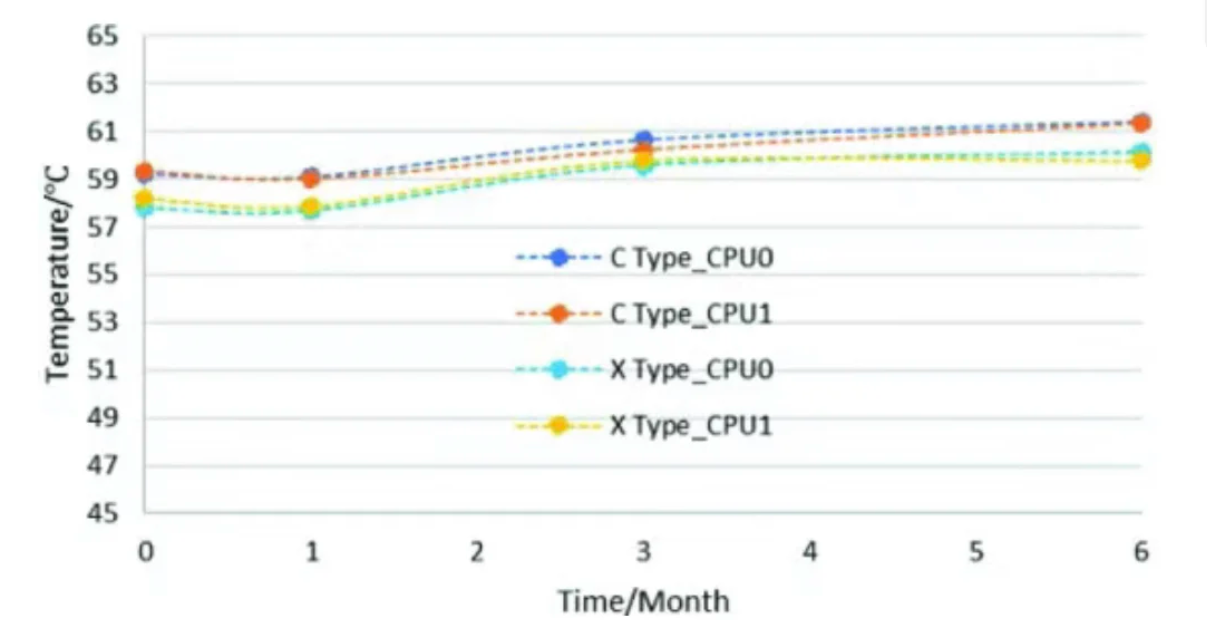
3. CPU DTS temperature monitoring: C
PU is a critical component, and its temperature judgment is regularly recorded to assess its impact on performance and reliability. Three servers with three different water tanks were selected for investigation. The average CPU temperature trends in the C-type and X-type immersion liquids for the 0/-1/-3/-6 months showed no significant decrease in CPU temperature in both immersion liquids. The temperature fluctuation of the CPU in the third month was caused by the CPU DTS reading tolerance and immersion fluid Fw update, and the pump speed was reduced from 70% to 62%, resulting in power saving. This proves that the cooling solution (radiator and TIM) has almost no negative impact on CPU performance and reliability.
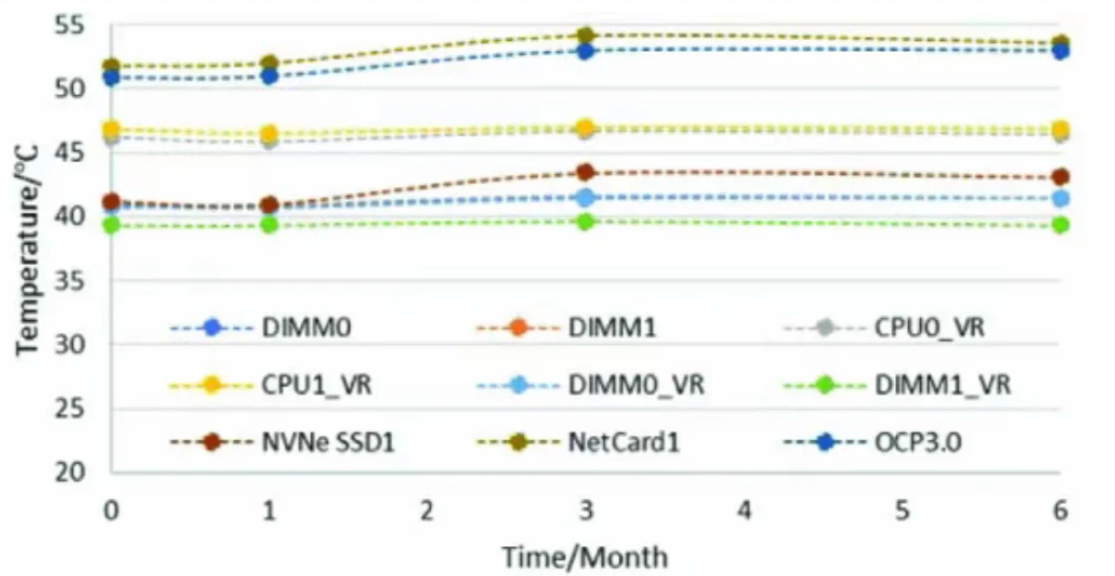
4. Temperature monitoring of other key components:
Record the operating temperatures of key components such as DDR, VRM, PCH, and NIC in the server system. The average temperature trend of these components in the C-type and X-type immersion liquids during the months of 0/-1/-3/-6 is the same as that of the CPU temperature trend, with no significant decrease over time.
CPU cooler recommendation:
If you have a high-end CPU and want to achieve optimal cooling performance while maintaining quietness, you can choose the following CPU coolers.
XTT-09 CPU cooler: Provides top-notch cooling performance, outperforming high-end competitors such as Noctua's D15S, while reducing costs by nearly 2/3.
XTT-01 CPU cooler: It provides excellent aesthetics, powerful cooling performance, and quiet noise levels
XTT-07 CPU cooler: Combining excellent performance, minimal noise levels, and affordability.
XTT-12 CPU cooler: It is one of the best performing air coolers we have tested. It runs silently.
Why can you trust us at sz-xtt.com?
Our expert reviewers from Shenzhen Xintongtai Technology Co., Ltd. will spend several hours taking you to a detailed understanding and comparison of our product performance, so that you can choose the most suitable product information content for your needs.
